|
a team of engineers at the ucla henry samueli school of engineering and applied science demonstrated that by adding nanoscale aluminum oxide particles during the melting of nickel that it increased the depth of the melting zone by 68 percent and decreased the heat-affected zone by 67 percent. the same results were achieved using silicon carbide nanoparticles as well.
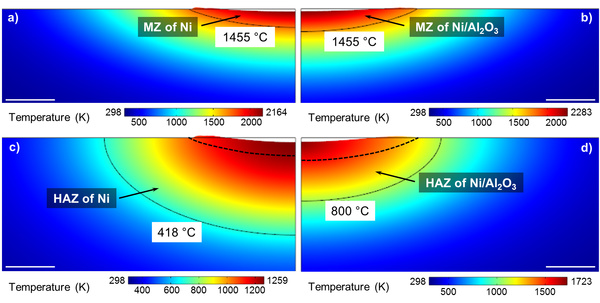
adding nanoscale particles of aluminum oxide during a later melting of nickel increases the depth of the metal’s
melting zone by 68 percent, while decreasing the heat-affected zone by 67 percent. (ucla)
this discovery could have huge ramifications in manufacturing, according to a report on the ucla website. the melting zone is the region where metal turns to liquid and spreads into the molds provided by the manufacturer, while the heat-affected zone is adjacent to the melting zone and is where the metal is not molten but could be deteriorating from the heat.
typically, the size of the melting zone is matched by the heat-affected zone, but that is something manufacturers would prefer not to see. optimally, the melting zone would be maximized with a minimal heat-affected zone. this would lower the possibility of defects in the metal of the heat-affected zone.
the addition of nanoparticles lowers the amount of heat that is dissipated, which makes the melting zone deeper without heat spreading into the adjacent areas. the nanoparticles reduce thermal conductivity to “trap” the heat in the melting zone and they also increase the viscosity of the molten metal to suppress thermocapillary flow.
this technique could alter the manufacturing and 3-d printing processes by increasing the stability of the material in the heat-affected zones. it could be used in the fabrication of lightweight, high-performance parts or precision components.
the scientists believe that this discovery of nanoparticles changing the process of melting and solidification will not only benefit manufacturing but also pharmaceutical and energy storage applications.
the research was recently published in nature communications. the abstract of the report read:
“effective control of melting and solidification behaviours of materials is significant for numerous applications. it has been a long-standing challenge to increase the melted zone (mz) depth while shrinking the heat-affected zone (haz) size during local melting and solidification of materials.
“in this paper, nanoparticle-induced unusual melting and solidification behaviours of metals are reported that effectively solve this long-time dilemma. by introduction of al2o3 nanoparticles, the mz depth of ni is increased by 68%, while the corresponding haz size is decreased by 67% in laser melting at a pulse energy of 0.18 mj.
“the addition of sic nanoparticles shows similar results. the discovery of the unusual melting and solidification of materials that contain nanoparticles will not only have impacts on existing melting and solidification manufacturing processes, such as laser welding and additive manufacturing, but also on other applications such as pharmaceutical processing and energy storage.”
|